Data Analysis for LEL - Week 5
Statistical variables
University of Edinburgh
Sample \(y\)

When we ask a research question, we collect a sample \(y\) from a population.
Sample \(y\)
\(y\) is a sample of values (\(y_1, y_2, y_3, ..., y_n\)).
Sample of values can be e.g.:
Number of telic and atelic verbs in a historical corpus of Sanskrit.
Voice Onset Time of stops from 50 speakers Mapudungun.
Friendliness ratings of synthetic speech as indicated by 300 participants.
…
Sample \(y\)
\(y\) is a sample of values (\(y_1, y_2, y_3, ..., y_n\)).
We say that the values in the sample \(y\) were generated by a (random) variable \(Y\).
Variable \(Y\)
\(Y\) is a (random) variable that generates the values in the sample \(y\).
A (statistical) variable is any characteristics, number, or quantity that can be measured or counted
When you observe or measure something, you are taking note of the values generated by the variable.
It’s called variable because it varies (ha!).
The opposite of a variable is a constant.
Sample \(y\)
\(Y\) is a (random) variable that generates the values in the sample \(y\).
Variables can be e.g.:
Token number of telic verbs and atelic verbs in written Sanskrit.
Voice Onset Time of stops in Mapudungun.
Friendliness ratings of synthetic speech.
…
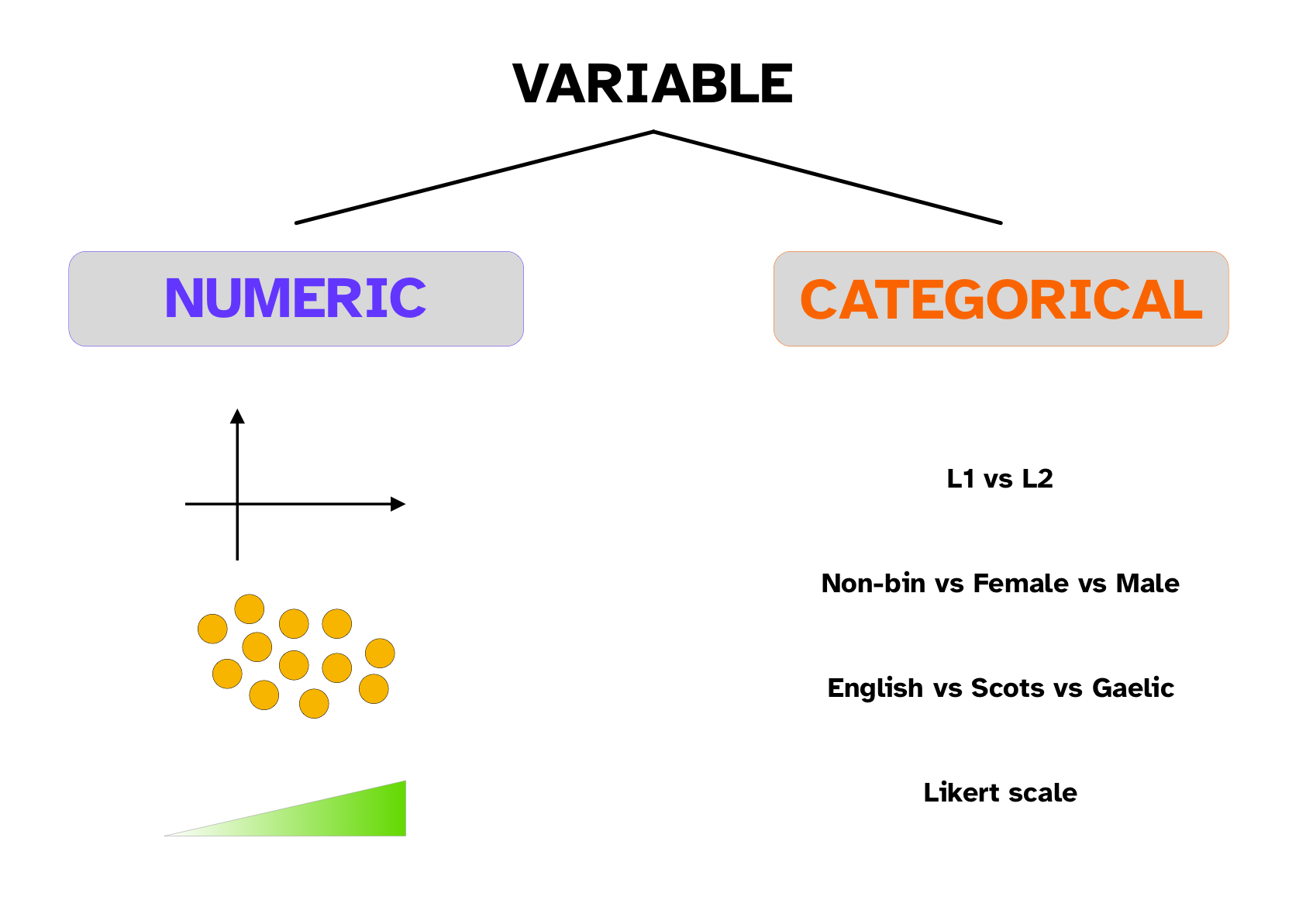
Types of variables
Types of variables
Types of variables
Numeric continuous variable: between any two values there is an infinite number of values.
The variable can take on any positive and negative number, including 0.
The variable can take on any positive number only.
Proportions and percentages: The variable can take on any number between 0 and 1.
Numeric discrete variable: between any two consecutive values there are no other values.
- Counts: The variable can take only on any positive integer number.
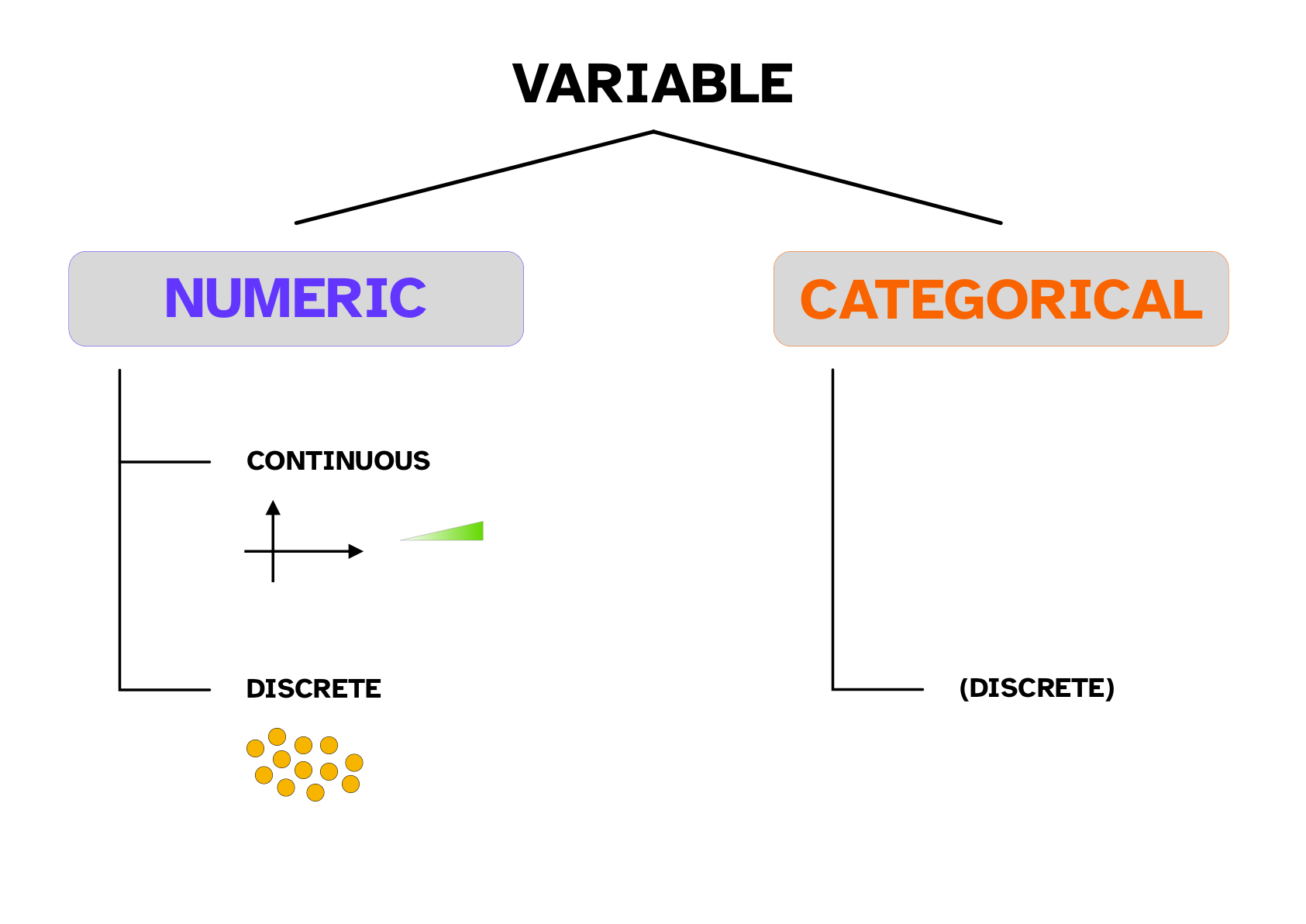
Types of variables
Categorical (discrete) variable.
Binary or dichotomous: The variable can take only one of two values.
The variable can take any of three of more values.
Ordinal: The variable can take any of three of more values and the values have a natural order.
Operationalisation
We can operationalise something as a numeric or a categorical variable.
Think of ways to operationalise the following:
Voice Onset Time.
Friendliness of speech.
Lexical frequency.
…
Operationalisation
Summary
The sample \(y\) is generated by a (random) variable \(Y\).
A (statistical) variable is any characteristics, number, or quantity that can be measured or counted.
Variables can be numeric or categorical.
- Numeric variables can be continuous or discrete.
- Categorical variables are only discrete.
We operationalise a measure/observation as a numeric or a categorical variable.